What Causes Eczema? Understanding the Triggers and How to Manage Them
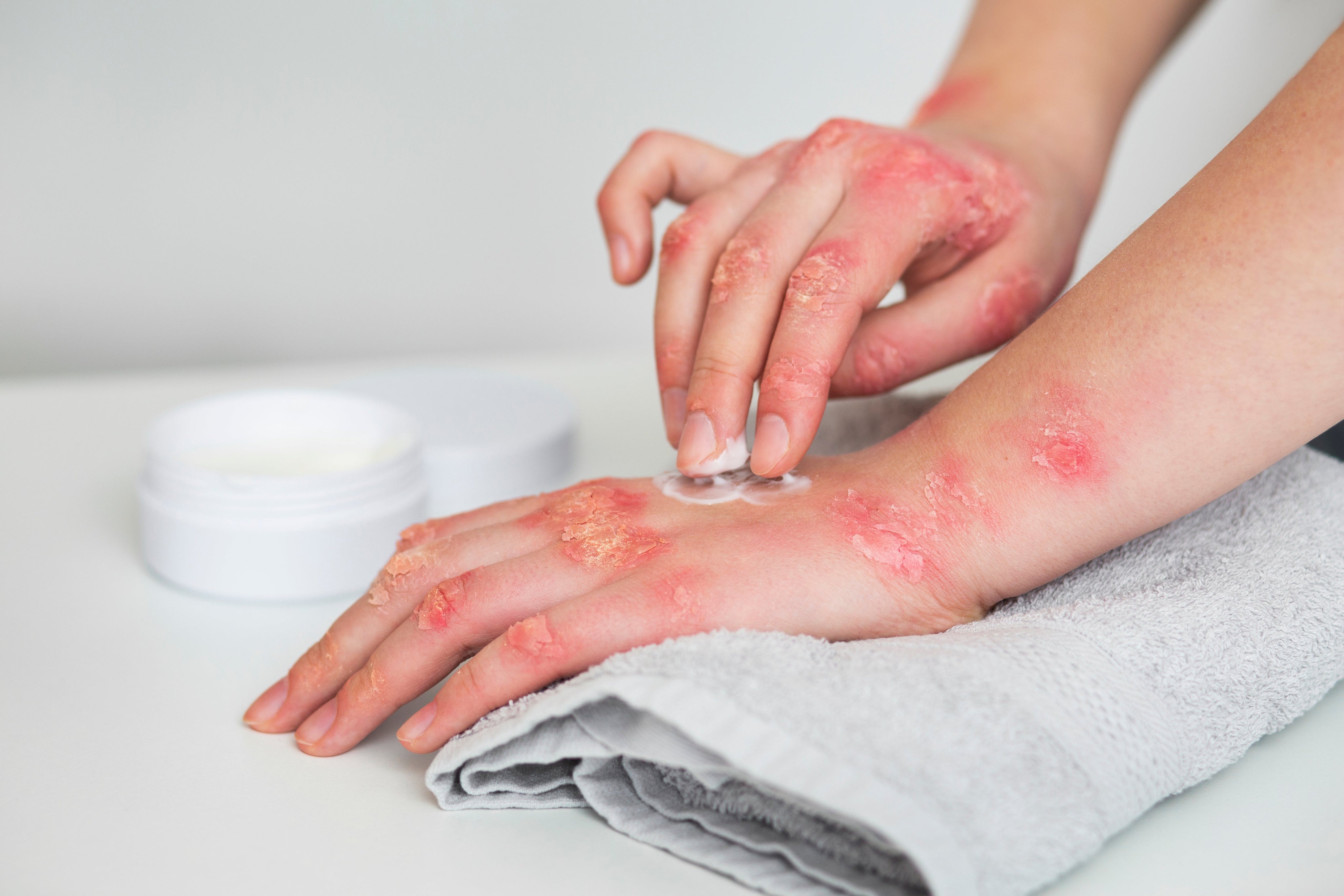
Understanding skin conditions like eczema is crucial for holistic care in a society increasingly focused on health and well-being. Eczema is a complex disorder that can profoundly impact quality of life, leaving many seeking clear answers. This article delves into the causes and triggers of eczema, offering insights into its origins and effective management strategies. By examining its symptoms, triggers, and treatment options, we aim to provide a comprehensive guide that educates and empowers individuals to enhance their skin health.
What is Eczema
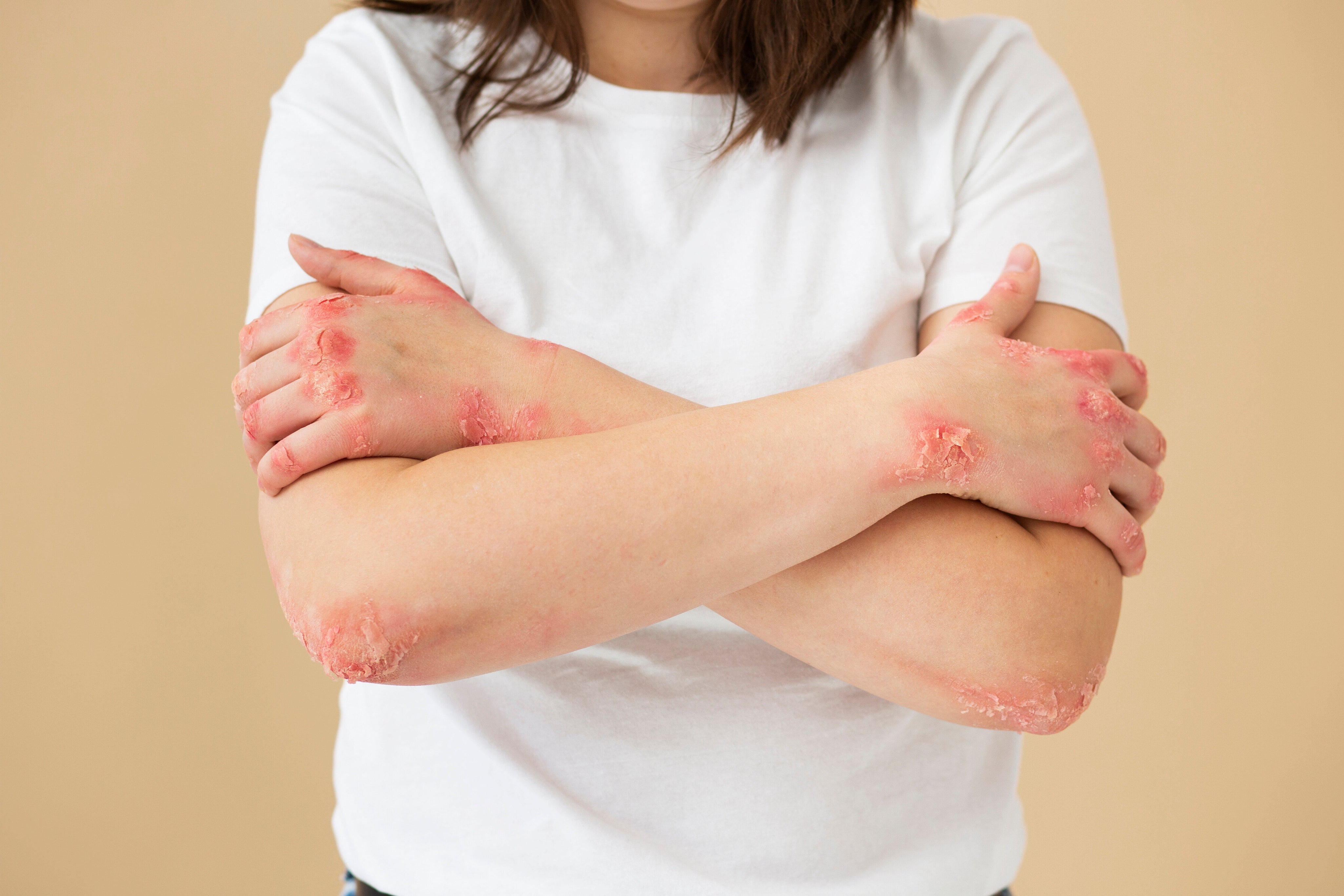
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterised by red, itchy, and inflamed patches on the skin. It often begins in childhood but can occur at any age. Understanding its causes and triggers is crucial for effective management.
Symptoms of Eczema
The symptoms of eczema can vary from person to person, but they typically include:
1. Dry Sensitive Skin
Eczema often leads to dry skin that is sensitive to touch, contributing to discomfort.
2. Red, Inflamed Patches
Affected areas may appear red and swollen, often exacerbating the itchiness.
3. Intense Itching
One of the hallmark symptoms of eczema is the intense urge to scratch, which can worsen the condition.
4. Rough, Scaly Skin
Skin affected by eczema may become rough and scaly, losing its smooth texture.
5. Blisters or Oozing
In some cases, blisters can form and ooze, leading to potential infections.
6. Thickened, Cracked Skin
Chronic scratching can cause the skin to thicken and crack, creating a cycle of irritation.
7. Dark or Discolored Patches
Long-term eczema can lead to hyperpigmentation or darker patches on the skin.
8. Swelling
Inflammation can result in swelling around the affected areas.
Common Causes and Triggers of Eczema
Understanding the root causes of eczema can help manage and prevent flare-ups. Here are some common triggers:
1. Genetics
A family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma can significantly increase the likelihood of developing eczema. If close relatives have these conditions, it may indicate a genetic predisposition that makes individuals more susceptible to skin issues.
2. Immune System Response
Eczema is often linked to an overactive immune response. When the immune system reacts strongly to allergens or irritants in the environment, it can lead to inflammation and flare-ups of eczema, resulting in red, itchy patches on the skin.
3. Environmental Irritants
Exposure to various environmental irritants plays a crucial role in triggering eczema. Harsh soaps, detergents, and pollutants can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to irritation and increased sensitivity. It's essential to identify and minimize contact with these irritants to manage symptoms effectively.
4. Sweat and Heat
Increased sweating and heat are common culprits that can exacerbate eczema symptoms, particularly in warmer climates. When the body overheats, sweat can irritate the skin and lead to intense itching and discomfort. Managing temperature and staying cool can help alleviate these symptoms.
5. Food Allergies
Certain food allergies, especially those related to dairy and nuts, can trigger eczema flare-ups in some individuals. Identifying and avoiding these allergens through an elimination diet may be beneficial for managing eczema symptoms and maintaining skin health.
6. Stress
Emotional and psychological stress can significantly impact skin health, often triggering or worsening eczema. This highlights the important connection between the mind and skin, suggesting that stress management techniques, such as mindfulness or relaxation exercises, can play a role in alleviating symptoms.
7. Clothing and Fabrics
The type of clothing and fabrics worn can also affect eczema. Irritating materials like wool or synthetic fibers can lead to increased itching and discomfort. Opting for soft, breathable fabrics like cotton and avoiding tight-fitting clothes can help reduce irritation and improve overall comfort for those with eczema.
Eczema Facts
1. Eczema is not contagious.
This means you cannot catch it from someone else, allowing those affected to interact freely without fear of spreading the condition.
2. It affects about 10-20% of children and 1-3% of adults.
These statistics highlight the prevalence of eczema, making it one of the most common skin conditions, especially among young children.
3.Common triggers include allergens, irritants, and stress.
Allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can provoke flare-ups, while irritants such as soaps and detergents can exacerbate the condition. Emotional stress is also a significant factor that can influence the severity of symptoms.
4. Eczema can be managed with proper skincare and medication.
A consistent skincare routine that includes moisturizing and the use of prescribed medications can help alleviate symptoms and keep flare-ups at bay.
5. It often appears as red, inflamed patches on the skin.
These patches can vary in size and may occur on various parts of the body, including the face, hands, and behind the knees, often leading to discomfort.
6. People with eczema may experience itching and dryness.
The intense itchiness can lead to scratching, which may worsen the condition and lead to skin damage or infection, making effective management crucial.
7. The condition can be hereditary, running in families.
If one or both parents have eczema, asthma, or hay fever, their children are at a higher risk of developing eczema, suggesting a genetic link.
8. There are different types of eczema, including atopic dermatitis and contact dermatitis.
Atopic dermatitis is the most common form, often starting in childhood, while contact dermatitis occurs when the skin reacts to specific substances, underscoring the need for individualized treatment.
9. Eczema symptoms can vary seasonally, with some individuals experiencing flare-ups during winter when the air is dry, and others in summer due to heat and humidity.
This variability can make it challenging for individuals to predict and manage their symptoms, requiring adaptability in their skincare approach.
Read More: How to Manage Seasonal Eczema Flare-Ups: Tips for Winter and Summer.
10.Beyond physical discomfort, eczema can impact mental health, contributing to issues like anxiety, depression, and poor sleep quality due to itchiness and irritation.
The constant battle with discomfort can lead to a decrease in quality of life, emphasizing the need for comprehensive care that addresses both physical and emotional well-being.
11. While there is no cure for eczema, many treatments are available that can effectively manage symptoms, including topical corticosteroids, moisturisers, and advanced biologic medications.
These treatments aim to reduce inflammation and restore the skin barrier, providing relief from symptoms and helping individuals lead a more comfortable life.
12. A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, may help improve overall skin health and reduce the frequency of eczema flare-ups.
Nutrition plays an essential role in skin health, and maintaining physical fitness can enhance overall well-being, all of which contribute to managing eczema more effectively.
13. Long-term and poorly managed eczema can lead to complications such as skin infections, highlighting the importance of seeking medical advice and following a tailored skincare regimen.
Regular consultations with healthcare providers can ensure that individuals receive the most effective treatments and strategies to prevent complications, ensuring better skin health and overall quality of life.
People at Risk for Eczema
1. Individuals with a family history of eczema or allergies
People with a family history of eczema or allergies may inherit a genetic predisposition to these conditions. This means that if close family members have experienced eczema, asthma, or allergic reactions, individuals may be more vulnerable to developing similar issues themselves.
2. People living in urban areas with higher pollution levels
Urban residents often face increased exposure to air pollution, which can exacerbate skin conditions like eczema. Pollutants can irritate the skin barrier, leading to inflammation and a higher likelihood of allergic reactions, making these individuals more susceptible to developing eczema.
3. Those with a weakened immune system, such as people with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy
Individuals with weakened immune systems have a reduced ability to fight off infections and respond to allergens. Conditions such as HIV/AIDS or treatments like chemotherapy can compromise immune function, making these individuals more prone to skin issues, including eczema.
4. People working in industries prone to skin irritants, such as healthcare workers or hairdressers
Certain professions expose individuals to skin irritants, including chemicals, soaps, and frequent handwashing. Healthcare workers and hairdressers are often in contact with substances that can trigger skin reactions, increasing their risk of developing conditions like eczema.
5. Individuals with other existing skin conditions, like psoriasis or rosacea
People who already have skin conditions such as psoriasis or rosacea may have a compromised skin barrier or heightened sensitivity. This pre-existing vulnerability can make them more likely to experience eczema, as their skin may be more reactive to external irritants and allergens.
6. Babies and young children, especially those with parents who smoke
Babies and young children have delicate skin that is more susceptible to irritants. Additionally, exposure to secondhand smoke can increase the risk of developing eczema, as it may provoke allergic reactions and irritate their sensitive skin. Children with parents who smoke should be monitored for skin conditions closely.
Treatment Options for Eczema
Managing eczema often requires a combination of treatments:
1. Moisturisers and Emollients
Regular application of moisturisers is essential for maintaining skin hydration and barrier function. By locking in moisture, these products help prevent dryness and keep the skin supple, which is crucial for individuals with conditions like eczema or psoriasis. Look for emollient-rich formulations that provide long-lasting hydration throughout the day.

2. Topical Steroids
Topical steroids are effective treatments for reducing inflammation and itchiness during flare-ups. These anti-inflammatory medications can quickly soothe irritated skin and help restore its normal appearance. It's important to follow a healthcare provider's recommendations regarding the strength and duration of use to avoid potential side effects.
3. Antihistamines
Antihistamines can be particularly helpful in alleviating itching, especially at night when the urge to scratch may disrupt sleep. By blocking histamine receptors, these medications reduce the sensation of itching, allowing for more restful nights. Consider discussing both over-the-counter and prescription options with your healthcare provider to find the right fit.
4. Light Therapy (Phototherapy)
Light therapy, or phototherapy, is a treatment that utilises UV light to help reduce symptoms and inflammation associated with various skin conditions. This method can be highly effective for individuals who have not responded to conventional treatments. Sessions are typically conducted under medical supervision to ensure safety and efficacy, making it a valuable addition to a comprehensive treatment plan.
5. Calcineurin Inhibitors
Calcineurin inhibitors are non-steroidal medications that can help reduce inflammation and itchiness without the side effects commonly associated with topical steroids. These prescription creams or ointments work by modulating the immune response in the skin, making them a suitable option for long-term management of chronic conditions. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment approach for your specific needs.
6. Topical Postbiotic and Prebiotic
Recent studies have investigated the use of topical postbiotic and prebiotic products as a potential treatment option for eczema. These formulations contain beneficial bacteria, enzymes, and nutrients that can help balance skin microbiome and promote healthier skin barrier function. While more research is needed, incorporating these types of products into your skincare routine may provide added benefits in managing eczema symptoms.

When to Consult a Professional
If you are experiencing severe or persistent eczema that negatively impacts your quality of life, it’s crucial to seek guidance from a healthcare professional. They can assess your condition and create a personalised treatment plan tailored towards addressing your eczema breakouts. This may include a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and skincare routines to effectively manage your symptoms and improve your overall well-being. Don’t hesitate to reach out for help—your health and comfort are important!
Discover Your Path to Holistic Wellness with Skin to Heart
At Skin to Heart, we understand the deep connection between your skin health and overall well-being. Our bespoke approach brings together cutting-edge skin solutions and holistic lifestyle practices tailored to your unique skin needs. Whether you're struggling with eczema, seeking enriched skincare insights, or looking to cultivate a harmonious balance between mind and body, our team of experts is here to guide you every step of the way. Explore our tailored treatments today and embark on your journey towards radiant, healthy skin and enhanced quality of life. Book a consultation with us and let's transform your skincare routine into a comprehensive wellness experience.
Eczema FAQs
What is the biggest cause of eczema?
The biggest cause of eczema is often linked to genetics and an overactive immune system response to environmental irritants.
Is eczema curable?
While there is no cure for eczema, effective management strategies can help control symptoms and minimise flare-ups.
Can eczema spread?
Eczema itself is not contagious, but the symptoms can worsen or spread to different areas of the skin if triggered.
0 comments


