Acne Duration, Treatment, Causes, and Prevention

What is Acne?
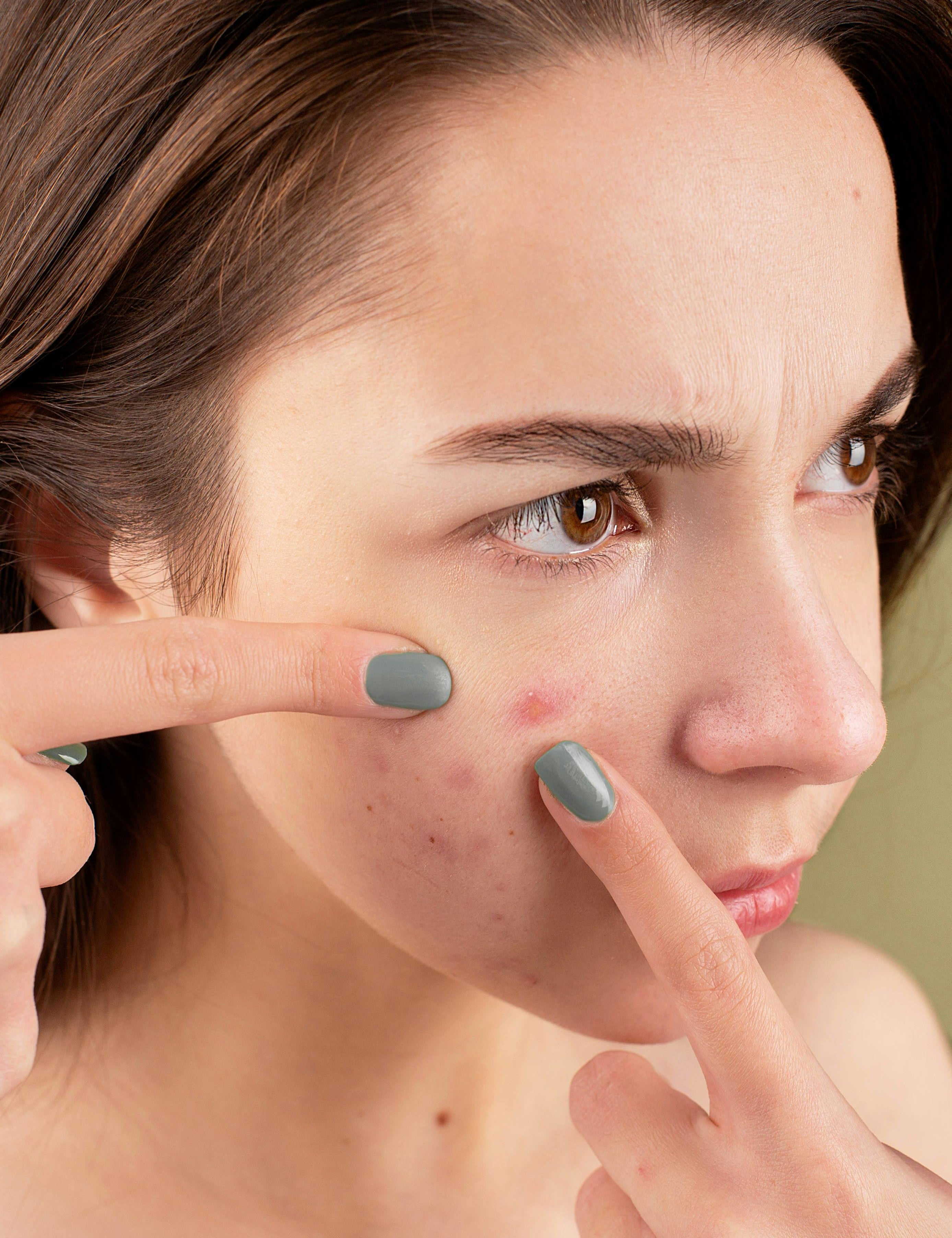
Acne is a prevalent skin condition that arises when hair follicles become obstructed with oil and dead skin cells. This often manifests as whiteheads, blackheads, or blemishes, typically appearing on the face, forehead, chest, upper back, and shoulders. While acne is most common among teenagers and young adults, it can affect individuals of all ages.
How Does Acne Go Away?
Acne can go away with proper treatment and care, and I'm excited to share how this journey can unfold. The healing process involves:
- Reducing inflammation — think of it as soothing your skin's stress.
- Keeping the skin clean — a simple yet vital step in your skincare routine.
- Using topical or oral medications to treat bacteria and excess oil — targeted solutions for clearer skin.
- Applying topical products to ensure your skin remains strong and healthy — like giving your skin a nourishing hug.
- And most importantly, patience — because true healing takes time, sometimes weeks to months, but every step forward is progress.
Remember, you're not alone in this. We're in this journey together, embracing every opportunity to improve our skin health and overall well-being.
Common Treatment and Prevention for Acne
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Benzoyl Peroxide
Benzoyl peroxide is a distinguished solution that eliminates acne-causing bacteria and regulates excess oil. Its meticulous action of removing dead skin cells ensures pores remain clear, fostering a refined and blemish-free complexion.
Salicylic Acid

Salicylic acid is a beta hydroxy acid (BHA) penetrates deeply to exfoliate and unclog pores from within, gently shedding dead skin cells and reducing inflammation. It’s a harmonious blend of science and luxury for clear,
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs)

AHAs, such as glycolic acid and lactic acid, work by exfoliating the skin's surface. These potent ingredients exfoliate the skin’s surface, removing dead skin cells and encouraging the growth of new, smoother skin. This process not only enhances the appearance of acne but also prevents future breakouts, ensuring a pristine and polished complexion.
Prescription Medications - by GP or dermatologist
Antibiotics
Topical or oral antibiotics reduce acne by decreasing the amount of bacteria and reducing inflammation. Common antibiotics for acne include clindamycin and doxycycline.
Retinoids

Topical retinoids, such as tretinoin, adapalene, and tazarotene, offer a sophisticated solution to unclogging pores and preventing acne formation. Beyond these benefits, they enhance cell turnover and diminish inflammation, promoting a radiant complexion. For those facing severe acne, oral retinoids like isotretinoin present a holistic approach by reducing the size of oil glands and regulating skin cell shedding.
Hormonal Treatments
Hormonal treatments, including oral contraceptives and anti-androgens like spironolactone offer a refined solution for women experiencing acne related to hormonal fluctuations. These treatments elegantly harmonise hormone levels, naturally reducing oil production.
Skincare Routine for Combating and Preventing Acne
Cleansing

Using a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser twice a day helps remove excess oil, dirt, and makeup without irritating the skin.
Moisturising

Even acne-prone skin needs moisture. A non-comedogenic moisturiser helps maintain the skin's barrier and prevent the overproduction of oil.
Sun Protection

Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher protects the skin from UV damage, which can worsen acne and cause post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Skin to Heart Tip: Struggling to figure out what really helps with breakouts? Our guide, 8 Tested and Proven Treatments for Acne, breaks everything down simply.
Healthy Lifestyle
Balanced Diet
A refined diet abundant in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is essential for luminous skin health. Our commitment to holistic wellness is reflected in studies suggesting that reducing high-glycemic foods and dairy can significantly enhance complexion clarity.
Stress Management
Stress, a known catalyst for hormonal imbalances, can surge oil production and trigger acne. Through our sophisticated mindfulness techniques, exclusive exercise regimens, and the promise of restorative sleep, we manage stress levels with unparalleled precision.
Adequate Sleep
Quality sleep is a cornerstone of our approach, facilitating the body's natural ability to repair and regenerate skin cells. Recognising the detrimental impact of poor sleep on stress hormones and skin health, we advocate for a regimen that nurtures both body and soul.
Common Causes of Acne
Acne, often viewed as a superficial concern, stems from a rich tapestry of internal and external factors. Understanding these causes and triggers is paramount to crafting effective treatments and a holistic prevention plan. Let's journey through the multifaceted origins of acne:
1. Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations are pivotal in acne development, especially during life's significant stages such as puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. Androgens, the male hormones present in both genders, stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more oil. This excess oil, combined with dead skin cells, can clog pores and lead to breakouts. Hormonal imbalances also amplify inflammation and acne severity.
2. Genetic Predisposition:
Genetics can predispose individuals to acne by influencing sebum production, inflammation response, and the tendency for clogged pores. If one or both parents had acne, their offspring are more likely to face similar skin challenges. While genetics lay the foundation, environmental factors and lifestyle choices can modulate the expression of acne-related genes.
3. Medications and Cosmetics:
Certain medications and cosmetic products may exacerbate acne or trigger breakouts in susceptible individuals. Medications containing corticosteroids, androgens, or lithium are known culprits. These can stimulate oil production, alter hormone levels, or induce inflammation, all contributing to acne. Similarly, comedogenic (pore-clogging) ingredients in skincare and makeup can obstruct follicles and promote acne formation.
4. Dietary Factors:
While the direct link between diet and acne remains debated, emerging evidence suggests that dietary choices may influence acne severity and frequency. High-glycemic foods like sugary snacks, refined carbohydrates, and processed foods can elevate blood sugar and insulin levels, stimulating sebum production and inflammatory pathways, exacerbating acne. Additionally, dairy products contain hormones and growth factors that may impact skin health and contribute to acne development in some individuals.
5. Environmental Factors:
Environmental pollutants, UV radiation, humidity, and climate changes can impact skin health, predisposing individuals to acne. Airborne pollutants and particulate matter can accumulate on the skin, potentially clogging pores and triggering inflammation. UV radiation, initially drying out pimples and giving the illusion of improvement, can exacerbate acne long-term by increasing inflammation and hyperpigmentation. Humid environments create ideal conditions for bacterial growth and pore congestion, especially for those with oily or acne-prone skin.
6. Stress and Emotional Well-being:
Psychological stress, whether acute or chronic, influences acne through complex interactions between the nervous, endocrine, and immune systems. Stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can stimulate sebum production and inflammation, leading to acne exacerbation. Moreover, stress-related behaviors such as poor sleep, unhealthy dietary choices, and inadequate skincare practices can compound acne-related issues.
What NOT to Do for Acne Treatment and Healing
While addressing acne, it's equally crucial to avoid certain habits and practices that can worsen the condition:
1. Overwashing or Scrubbing:
Excessive cleansing or aggressive scrubbing can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to irritation and inflammation. This can disrupt the skin's barrier function and exacerbate acne. Choose gentle cleansers and avoid harsh scrubbing motions.
2. Picking or Popping Pimples:
As tempting as it may be, picking or popping pimples can introduce bacteria into the skin, prolong inflammation, and increase the risk of scarring. It can also spread infection to surrounding areas, triggering more breakouts. Allow pimples to heal naturally or seek professional extraction.
3. Using Harsh or Drying Products:
Skincare products containing alcohol, fragrances, or abrasive ingredients can irritate the skin and exacerbate acne. Avoid products that strip the skin of moisture, as this can prompt the sebaceous glands to produce more oil to compensate. Opt for gentle, non-comedogenic formulations suitable for acne-prone skin.
4. Ignoring Sun Protection:
Neglecting sun protection can worsen acne and exacerbate post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. UV radiation can induce inflammation and compromise the skin's healing process. Always use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, even on overcast days, and reapply regularly.
5. Stressing Over Acne:
While stress can exacerbate acne, fixating on breakouts and obsessively scrutinising the skin can further aggravate stress levels. Practice stress-management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing, or engaging in hobbies to promote relaxation and overall well-being.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many acne cases can be managed with OTC treatments and lifestyle changes, sometimes professional help is needed. Here are signs it's time to see a dermatologist:
1. Persistent or Severe Acne
If acne persists or is severe with deep, painful cysts, professional treatment is necessary. Severe acne can cause scarring and emotional distress.
2. Failed Home Treatments
If OTC products don't work or make acne worse, consult a dermatologist for personalised treatment.
3. Potential Scarring
Early intervention can prevent further scarring. Treatments like laser therapy, chemical peels, or microneedling can help.
4. Emotional Impact
If acne affects your self-esteem or mental health, seek support from a mental health professional or counselor.
5. Hormonal Imbalance
For hormonal acne linked to conditions like PCOS, see a healthcare provider for hormonal treatments.
6. Prescription Medications
For moderate to severe acne, prescription meds like antibiotics or retinoids may be needed under medical supervision.
7. Skin Sensitivity or Allergic Reactions
If you have adverse reactions to skincare products, stop use and consult a healthcare professional for alternatives.
8. Pregnancy or Nursing
If pregnant or breastfeeding, consult a healthcare provider before using acne treatments. Some may pose risks to the baby.
By recognising these signs and proactively seeking professional help, individuals can access expert guidance and tailored treatment plans to effectively manage acne and achieve clearer, healthier skin. Remember that addressing acne early and comprehensively can minimise long-term skin damage and improve overall well-being.
FAQs about Acne
Can ice remove pimples?
Ice can reduce inflammation and swelling, making pimples less noticeable, but it doesn't remove them.
Does drinking water help acne?
Staying hydrated helps maintain healthy skin, but water alone won't cure acne.
How to remove pimples overnight?
Applying spot treatments with benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid can reduce pimples overnight.
How to get clear skin?
A consistent skincare routine, a healthy diet, and avoiding known triggers are key to clear skin.
How do you heal a pimple fast?
Use a warm compress to reduce inflammation and apply an acne treatment product to speed up healing.
Can toothpaste remove pimples?
Toothpaste is not recommended for pimples as it can irritate the skin and cause more harm.
Can salt remove pimples?
Salt can dry out pimples, but it can also irritate and dry out the skin, leading to more issues.
Can lemon remove pimples?
Lemon has antibacterial properties but is too acidic and can irritate the skin, making acne worse.
How to remove pimples without using any products?
Maintain a clean face, use warm compresses, and avoid touching or picking at pimples to prevent irritation.
Is there a difference between acne and pimple?
While often used interchangeably, acne and pimples are not the same. Acne is a skin condition that encompasses a variety of blemishes, including blackheads, whiteheads, and cysts. A pimple, on the other hand, is a type of acne characterised by inflamed spots that are often red and filled with pus.
Achieve Clear Skin with Personalised Treatments from Skin To Heart
Ready to take control of your acne and achieve clear, radiant skin? At Skin To Heart, our consultations are more than just a routine—they are an exclusive experience where personal care and attention meet luxury. We invite you to book a consultation and embark on a transformative journey towards healthier, luminous skin. Your perfect complexion and a sense of community await, just a consultation away.
- Tags: acne
0 comments