Fungal vs. Bacterial Acne: How to Tell the Difference and Treat Each Type
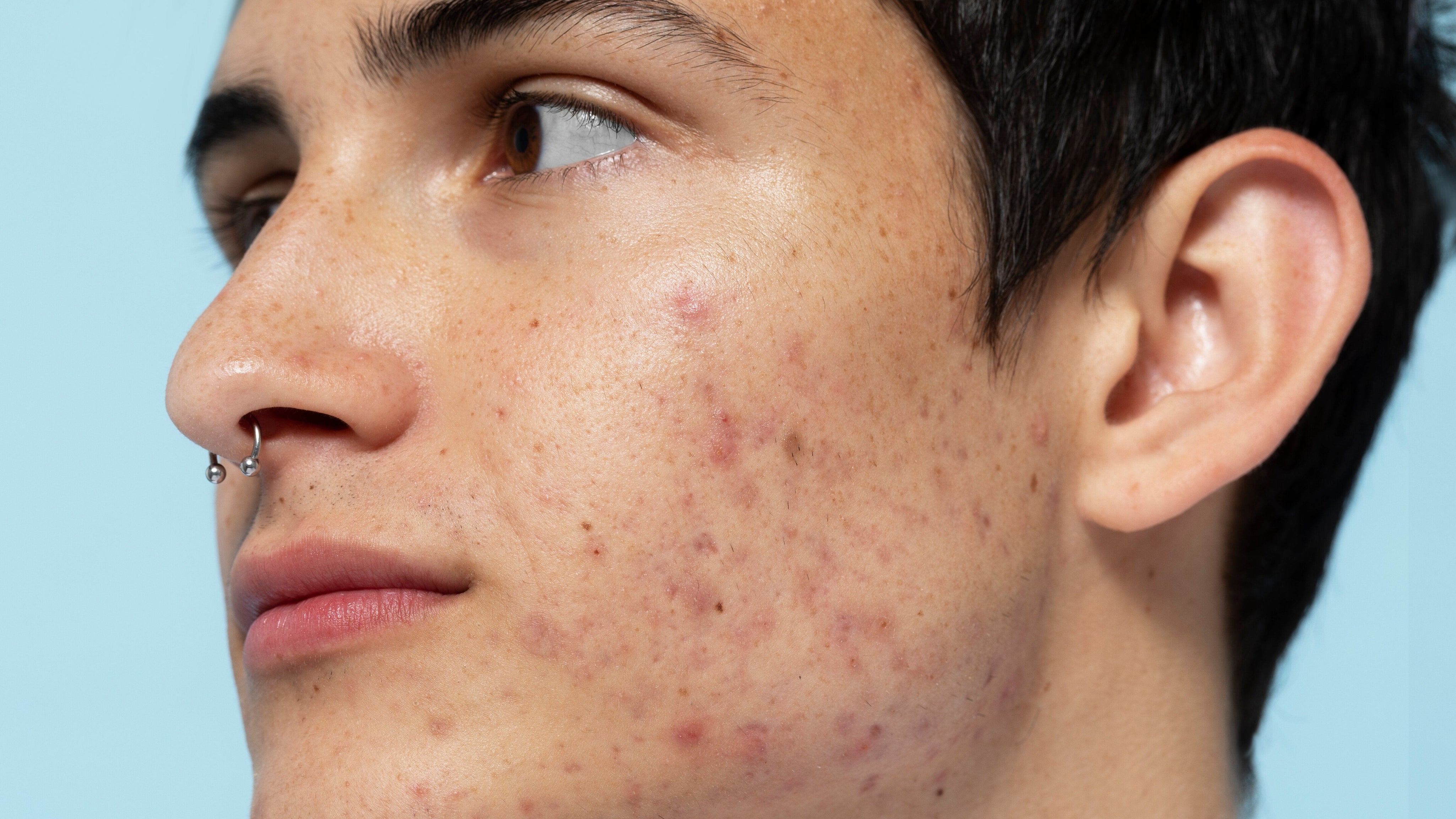
Acne can be a challenging skin condition to deal with, especially when it comes to distinguishing between fungal and bacterial acne. Understanding the differences, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for each type is crucial for effective management. In this expert guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about fungal and bacterial acne.
What is Fungal Acne
Fungal acne, also known as Malassezia folliculitis, is caused by an overgrowth of yeast (a type of fungus) that naturally occurs on the skin. It often appears in the form of small, itchy bumps and can be mistaken for traditional acne. Unlike bacterial acne, fungal acne typically thrives in warm, moist environments.
What is Bacterial Acne
Bacterial acne, commonly referred to simply as acne, is primarily caused by an overproduction of oil and bacteria, particularly Propionibacterium acnes, that clogs pores. This type of acne is characterized by the formation of blackheads, whiteheads, and inflammatory lesions like cysts and pustules.
Key Characteristics of Fungal vs Bacterial Acne
|
Feature
|
Fungal Acne
|
Bacterial Acne
|
|---|
|
Causes |
Malassezia (yeast) overgrowth |
Clogged pores and bacterial growth |
|
Appearance |
Small, uniform, itchy bumps |
Red, inflamed pimples, sometimes pus-filled |
|
Location |
Forehead, chest, and back |
Face, shoulders, and back |
|
Itchiness
|
Frequently itchy
|
Rarely itchy
|
Causes
Fungal Acne Cause
Fungal acne is triggered by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, often exacerbated by factors such as hormonal changes, excessive sweat, humid environments, and using certain skincare products that contain heavy oils.
Bacterial Acne Cause
Bacterial acne is caused by clogged pores due to excess oil and dead skin cells, leading to a proliferation of acne-causing bacteria. Factors such as hormonal changes, diet, and stress can also contribute to its development.
Related: Pre-Workout and Acne: Are They Really Connected?
Identifying Bacterial and Fungal Acne
Fungal Acne Symptoms
- Small, itchy bumps
- Often appears in clusters of relatively the same size
- Can worsen with heat and humidity
Bacterial Acne Symptoms
- Red, inflamed pimples
- Blackheads and whiteheads
- Can be painful and tender to the touch
Treatment Options for Fungal Acne vs Bacterial Acne
Given that bacterial and fungal acne stem from different underlying causes, it's important to explore the specific treatment methods for each concern. Here are some effective treatment options for both types:
Fungal Acne Treatment
- Oral antifungals: Medications like Fluconazole and Itraconazole can help eliminate the yeast causing the condition.
- Topical antifungal creams and shampoos: Products containing ingredients like clotrimazole or miconazole can effectively treat fungal acne.
- Shampoos with Zinc Pyrithione or Ketoconazole: These ingredients help reduce Malassezia on the skin.
Bacterial Acne Treatment
- Topical antibiotics: Clindamycin or erythromycin can help reduce inflammation and bacteria.
- Benzoyl peroxide: This common acne treatment kills bacteria and clears pores.
- Salicylic acid: Helps to exfoliate the skin and unclog pores.
- Isotretinoin: A powerful prescription medication for severe acne.
How to Rule Out Fungal Acne
To determine if your acne is fungal, pay attention to the following factors:
- Itchiness: Fungal acne often comes with a noticeable itch. If the bumps on your skin are itchy, it could indicate a fungal infection rather than traditional acne.
- Distribution: Fungal acne tends to appear in specific areas, often on the chest, back, or shoulders, and is usually uniform in size. In contrast, traditional acne can be more widespread or localized to the face.
- Humidity: Fungal acne can worsen in humid conditions, as the warm and moist environment promotes fungal growth. If you notice that your bumps become more prominent or irritating during hot, humid weather, it may signal a fungal issue.
By evaluating these factors, you can better understand the nature of your skin condition and seek appropriate treatment if necessary. If you suspect you have fungal acne, consulting a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan is always a good idea.
A dermatologist can also perform various tests to confirm the diagnosis, including skin biopsies, allergy tests, and cultures. These tests help determine the exact nature of the skin condition, allowing for a more accurate diagnosis and tailored acne treatment plan. By analysing skin samples or conducting specific assessments, dermatologists ensure that patients receive the most effective care for their unique situation.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you're struggling to manage your acne or are unsure whether it’s fungal or bacterial, consider consulting a dermatologist. They can provide a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan to help you achieve clear skin.
Get Clear Skin with Holistic Skin Care by Skin to Heart
Discover your journey to radiant skin with Skin to Heart's holistic approach to skin care. Our carefully selected products and personalised treatments address your skin concerns from the inside out, leaving you with a healthy and luminous complexion. Book an appointment with us today and let us help you achieve your skin goals!
0 comments

